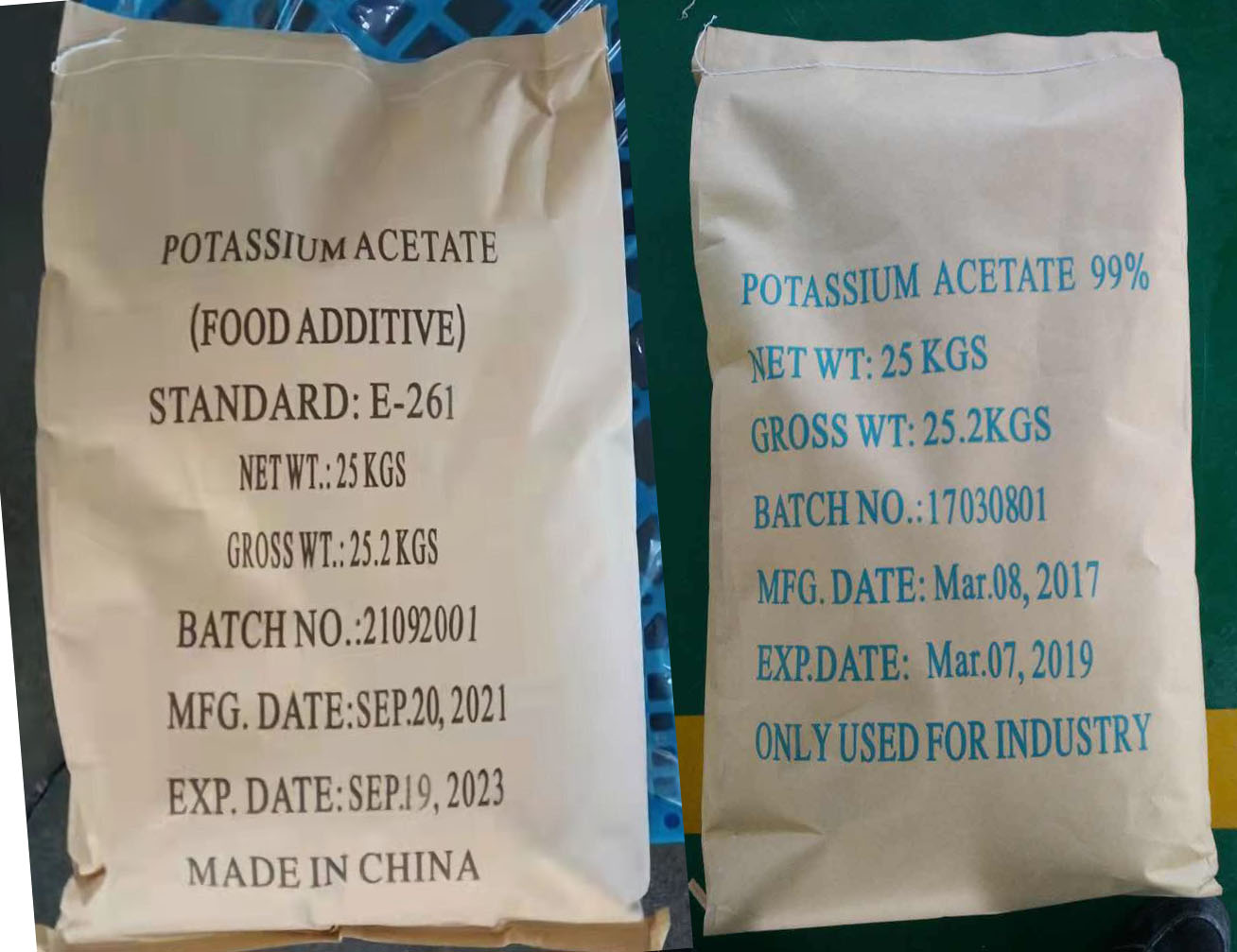
 Lactic acid is a versatile organic acid that plays a significant role in the food and feed industry. It is a naturally occurring compound formed during the fermentation process of sugars by lactic acid bacteria. Here is a detailed and comprehensive description of lactic acid in the food and feed industry:
Lactic acid is a versatile organic acid that plays a significant role in the food and feed industry. It is a naturally occurring compound formed during the fermentation process of sugars by lactic acid bacteria. Here is a detailed and comprehensive description of lactic acid in the food and feed industry:
**1. ** Formation and Sources:Lactic acid is produced through the fermentation of carbohydrates, such as glucose and lactose, by lactic acid bacteria. These bacteria can be found in various natural sources, including fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and fermented foods. The most common lactic acid-producing bacteria are Lactobacillus and Streptococcus.
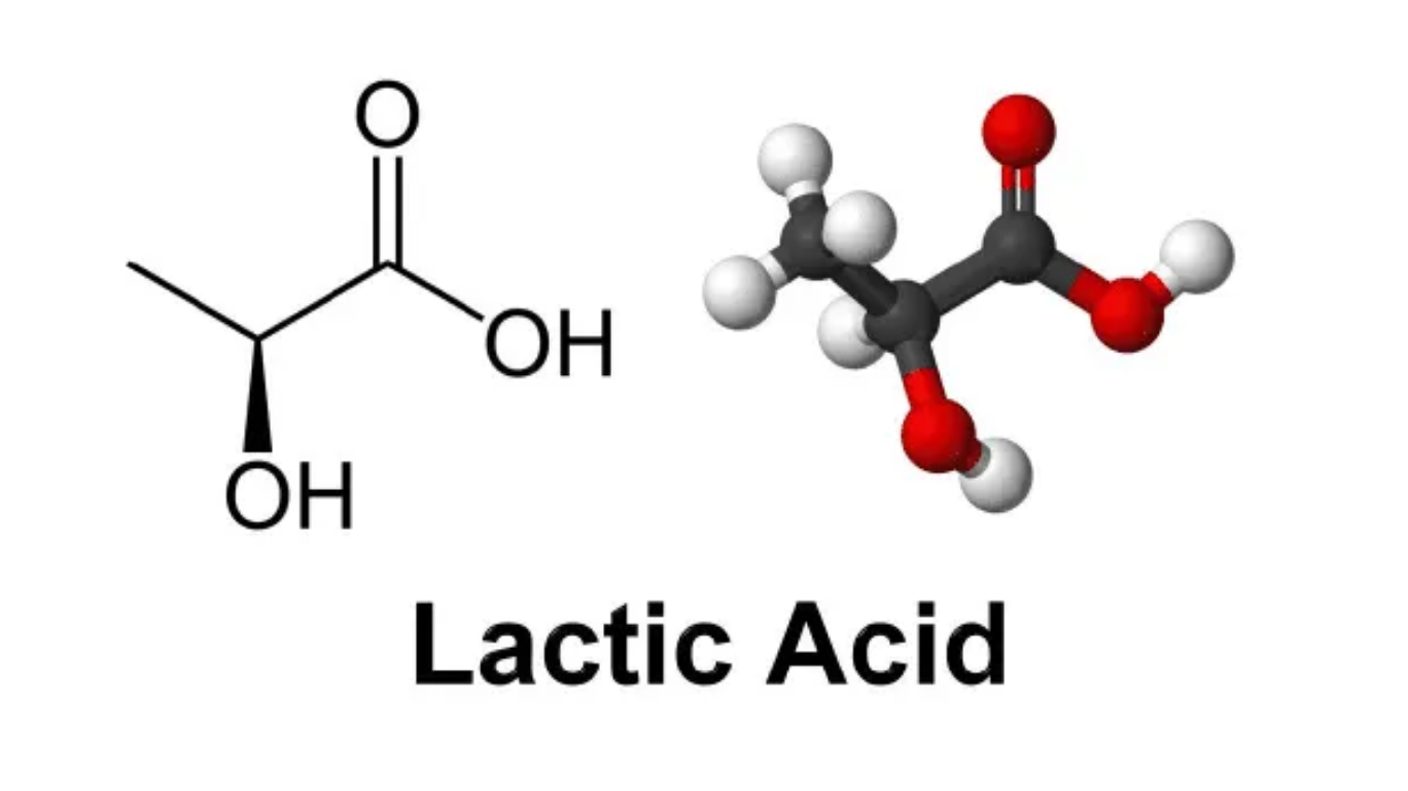
**2. ** Chemical Structure:Chemically, lactic acid is a hydroxy carboxylic acid. It exists in two optical isomers: L-lactic acid and D-lactic acid. L-lactic acid is the predominant form in natural fermentation processes. The chemical structure of lactic acid consists of a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a carbon atom.
**3. ** Uses in Food Industry:
Acidulant: Lactic acid is widely used as an acidulant in the food industry to enhance the tartness and acidity of various products. It is commonly found in sourdough bread, pickles, and sauerkraut.
Preservative: Lactic acid acts as a natural preservative, inhibiting the growth of spoilage microorganisms and extending the shelf life of certain foods.
Flavoring Agent: It contributes a mild, tangy flavor to fermented dairy products such as yogurt and buttermilk.
pH Regulator: Lactic acid helps regulate and stabilize the pH levels in food products, contributing to their overall quality.
**4. ** Functional Properties:
Gelling Agent: Lactic acid can be used in combination with other ingredients to form gels in certain food products, improving texture and consistency.
Emulsifying Agent: It has emulsifying properties, making it valuable in the production of salad dressings and mayonnaise.
Color Stability: Lactic acid can enhance the color stability of certain fruits and vegetables in processed foods.
**5. ** Uses in Feed Industry:
Feed Additive: Lactic acid and its salts (lactates) are used as feed additives for livestock. They serve as acidifiers, helping to create a more favorable pH environment in the digestive system and promoting animal health.
Antimicrobial Agent: Lactic acid exhibits antimicrobial properties, reducing the risk of pathogenic bacterial contamination in animal feed.
**6. ** Regulatory Considerations:
GRAS Status: Lactic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA).
**7. ** Production Methods:
Fermentation: The primary method of lactic acid production is through fermentation, where sugars are metabolized by lactic acid bacteria. This can be achieved through natural fermentation or controlled fermentation processes in industrial settings.
**8. ** Environmental Impact:
Biodegradability: Lactic acid is biodegradable, making it an environmentally friendly choice in various applications.