📌 Detailed Introduction of Silicon Carbide (SiC)
✔ What is Silicon Carbide?
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a high-hardness, chemically stable, and thermally resistant compound composed of silicon (Si) and carbon (C). It is widely used in abrasives, refractories, electronic components, and structural ceramics due to its exceptional strength, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
✔ CAS Number & Chemical Formula:
CAS Number: 409-21-2
Chemical Formula: SiC
Molecular Weight: 40.10 g/mol
📌 Product Specifications
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Black or green powder/grains |
| Purity (%) | ≥ 98.5% |
| Mohs Hardness | 9.2 – 9.5 |
| Melting Point (°C) | > 2,700°C (sublimes) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (120-270 W/m·K) |
| Electrical Resistivity | Varies by grade |
| Packing | 25kg bags, 1000kg jumbo bags |
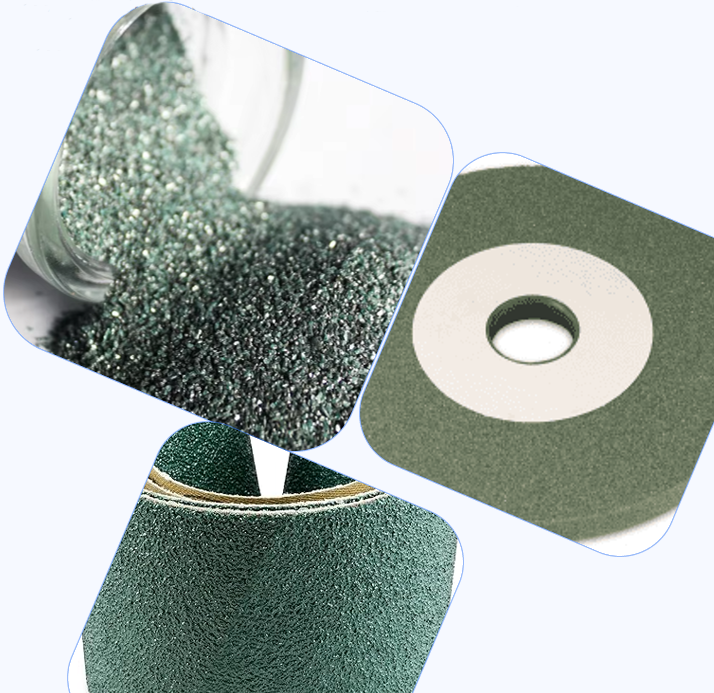
📌 Types of Silicon Carbide
✔ Black Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Hardness: Slightly lower than green SiC
Applications: Abrasives, grinding wheels, blasting media, cutting tools
✔ Green Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Higher purity than black SiC
Applications: Precision grinding, semiconductor manufacturing, ceramics
📌 Applications of Silicon Carbide (SiC)
✔ Abrasive & Cutting Tools Industry
Used in grinding wheels, cutting tools, sandpapers, and polishing compounds due to its extreme hardness.
Suitable for precision cutting of hard materials such as glass, ceramics, and metals.
✔ Refractory & Ceramic Industry
Applied in kiln furniture, crucibles, and furnace linings due to its high-temperature resistance and thermal shock stability.
Used in SiC ceramics for wear-resistant parts and structural components.
✔ Semiconductor & Electronics Industry
Silicon Carbide wafers are used in high-power, high-frequency electronic devices.
Key material for LEDs, power semiconductors, and high-efficiency solar cells.
✔ Metallurgical & Steel Industry
Used as a deoxidizer and desulfurizing agent in steel production.
Enhances thermal efficiency in metal foundries.
✔ Automotive & Aerospace Industry
Applied in SiC brake discs and lightweight composite materials for performance vehicles.
Used in heat shields, nozzles, and high-temperature-resistant parts in aerospace engineering.
📌 How Does Silicon Carbide Work?
Abrasive Effect:
With a Mohs hardness of 9.2 – 9.5, it efficiently grinds and polishes materials.
Heat & Chemical Resistance:
Withstands high temperatures above 2,700°C and remains stable in corrosive environments.
Electrical Properties:
Used as a semiconductor material for high-voltage and high-frequency applications.
📌 Production Method & Raw Materials
✔ Acheson Process (Carbothermal Reduction):
Raw Materials: Silica sand (SiO₂) + Carbon (C) (from petroleum coke).
Reaction: Heated in an electric resistance furnace at 1,600 – 2,500°C.
Formation: Silicon Carbide (SiC) crystals are formed and then crushed, purified, and processed into different grades.
📌 Famous Silicon Carbide Brands Worldwide
Saint-Gobain (France)
Washington Mills (USA)
Fiven (Norway)
Jiangsu Khonor Chemicals Co., Limited (China)
📌 Why Choose Jiangsu Khonor Chemicals Co., Limited?
✔ High-Purity Silicon Carbide (98.5% and above)
✔ Black & Green Silicon Carbide Available
✔ Custom Sizes and Packaging Options
✔ Strict Quality Control & International Compliance
📌 Order High-Quality Silicon Carbide (SiC) from Jiangsu Khonor Chemicals Co., Limited!
Looking for a trusted supplier of Silicon Carbide (SiC)? We provide premium-quality SiC products for abrasives, refractories, semiconductors, and industrial applications.
📞 Contact us today for a free quote & sample!
Silicon Carbide - Abrasive Material
1. Overview of Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a synthetic, hard, and crystalline compound composed of silicon (Si) and carbon (C). It is widely used as an abrasive material due to its exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability. Silicon carbide exists in various forms, including black SiC, green SiC, and bonded or coated abrasives.
2. Properties of Silicon Carbide as an Abrasive Material
Extreme Hardness: SiC has a Mohs hardness of about 9.2, making it one of the hardest materials after diamond and boron carbide.
High Thermal Conductivity: It can withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for high-speed grinding and cutting applications.
Chemical Resistance: SiC is resistant to acids and alkalis, allowing it to be used in harsh environments.
Sharp Cutting Edges: The crystal structure forms sharp, angular grains that provide efficient cutting action.
Brittle Nature: While extremely hard, SiC is brittle and fractures easily, which helps in constantly exposing new sharp edges during use.
3. Applications of Silicon Carbide as an Abrasive
SiC is commonly used in various forms, including:
Grinding Wheels: Used for precision grinding of hard materials such as ceramics, glass, and non-ferrous metals.
Abrasive Papers & Sanding Discs: Employed for surface finishing, metal polishing, and wood sanding.
Blasting Media: Used in sandblasting for surface cleaning and preparation.
Cutting Tools: SiC abrasives are used in saw blades and cutting discs for high-speed material removal.
Lapping & Polishing Compounds: Used in fine polishing of semiconductor wafers, optics, and precision tools.
Refractory Applications: SiC abrasives are also used in high-temperature furnaces and kiln linings.
4. Working Principle of Silicon Carbide as an Abrasive
Silicon carbide functions as an abrasive by utilizing its sharp, hard grains to cut into materials. The working principle is based on the following mechanisms:
Mechanical Cutting Action: The sharp SiC grains penetrate the material surface, breaking away small chips or particles.
Brittle Fracture: Due to its hardness, SiC can fracture under stress, continuously exposing new cutting edges, which enhances its abrasive effectiveness.
Heat Dissipation: Its high thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat, reducing the risk of overheating and workpiece damage.
Micro Fracturing: The abrasive grains fracture at a micro level, maintaining their sharpness and ensuring consistent performance.
5. How to Use Silicon Carbide Abrasives?
To maximize the efficiency of SiC abrasives, proper selection and usage are crucial:
Choosing the Right Grit Size:
Coarse (16-60 grit) for aggressive material removal.
Medium (80-220 grit) for general-purpose grinding and finishing.
Fine (240-1000+ grit) for polishing and precision work.
Selecting the Appropriate Form:
Use bonded SiC wheels for heavy grinding applications.
Coated SiC abrasives (sandpaper, belts) for surface finishing.
Loose SiC grains for lapping and polishing.
Adjusting Pressure and Speed:
Apply moderate pressure to prevent excessive heat buildup.
Use appropriate rotational speeds to balance efficiency and wear rate.
Cooling and Lubrication:
In wet grinding or polishing, water or oil-based coolants can enhance performance and reduce dust generation.
Proper Safety Precautions:
Use protective gear such as safety glasses, gloves, and dust masks.
Ensure adequate ventilation when working with SiC abrasives.
Conclusion
Silicon carbide is a highly effective abrasive material known for its hardness, sharpness, and heat resistance. It is widely used in grinding, cutting, polishing, and surface finishing applications. By selecting the appropriate grit size, form, and operating conditions, SiC abrasives can deliver excellent performance across a range of industrial and precision applications.